Removal of annoying skin lesions and warts in Frankfurt
Although warts and benign skin lesions are harmless from a medical point of view, they can cause cosmetic impairments. We use innovative approaches for the targeted treatment of viral warts and senile warts.
Our range of services includes proven procedures and advanced technologies such as laser therapy for efficient treatments. Laser medicine offers a simple and gentle solution for removing viral warts, senile warts and other benign skin lesions.
We understand that warts are not just cosmetic problems, but can also cause discomfort and discomfort. That is why we attach great importance not only to alleviating the symptoms, but also to sustainably combating the causes.
Find out more about (age-related) warts and our specialized services for treating these skin problems here or book an appointment for treatment directly at our dermatology practice in Frankfurt.
Warts on hands and feet (Verruca vulgares et plantares)
Viral warts are mainly localized on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, whitish to skin-coloured, usually the size of a pea.
Virus warts are transmitted through direct physical contact, smear contact or – if localized on the feet – indirectly via warm, damp surfaces such as bathroom mats, in swimming pools or in the sauna.
Due to the continuous strain on the soles of the feet, these grow into the depth of the heel or sole of the foot and can be painful when walking (so-called plantar warts).
Genital warts (Condylomata acuminata)
How do you treat viral warts?
There are various ways to treat viral warts.
Commercially available solutions or cold stamps are supposed to destroy the virus warts directly. As the viruses are not only located in the warts, but also microscopically in the skin, these treatment options are often not promising. The warts quickly grow back due to the virus residues present.
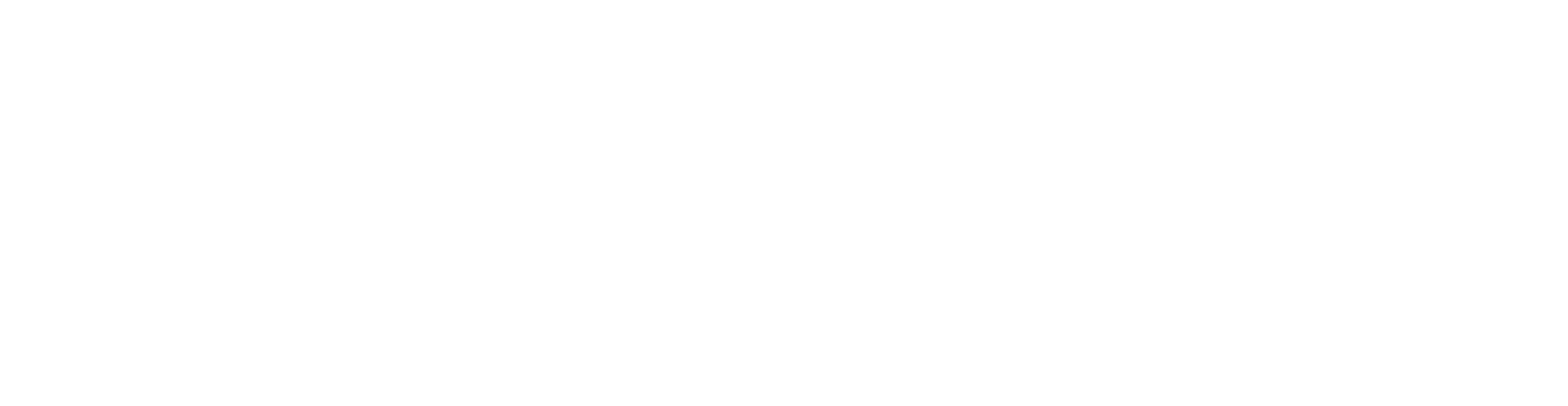
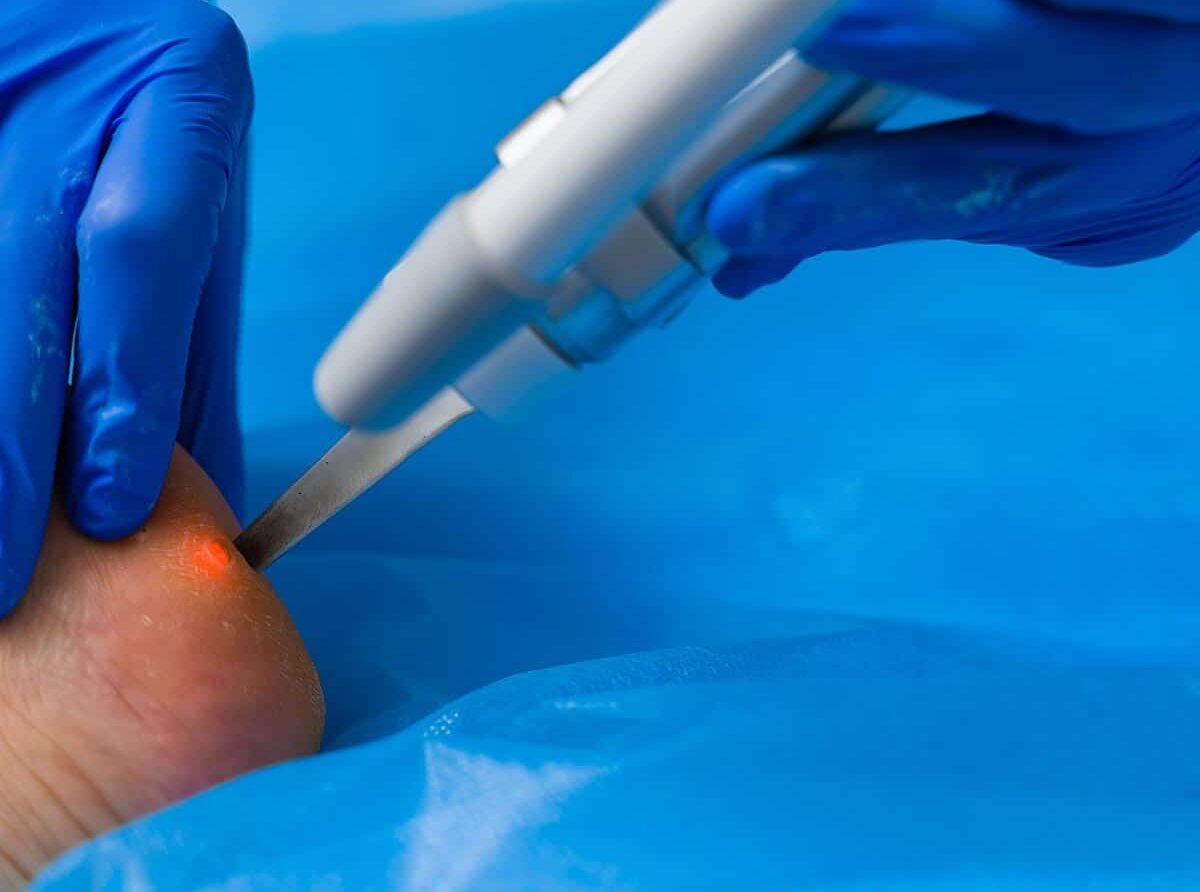
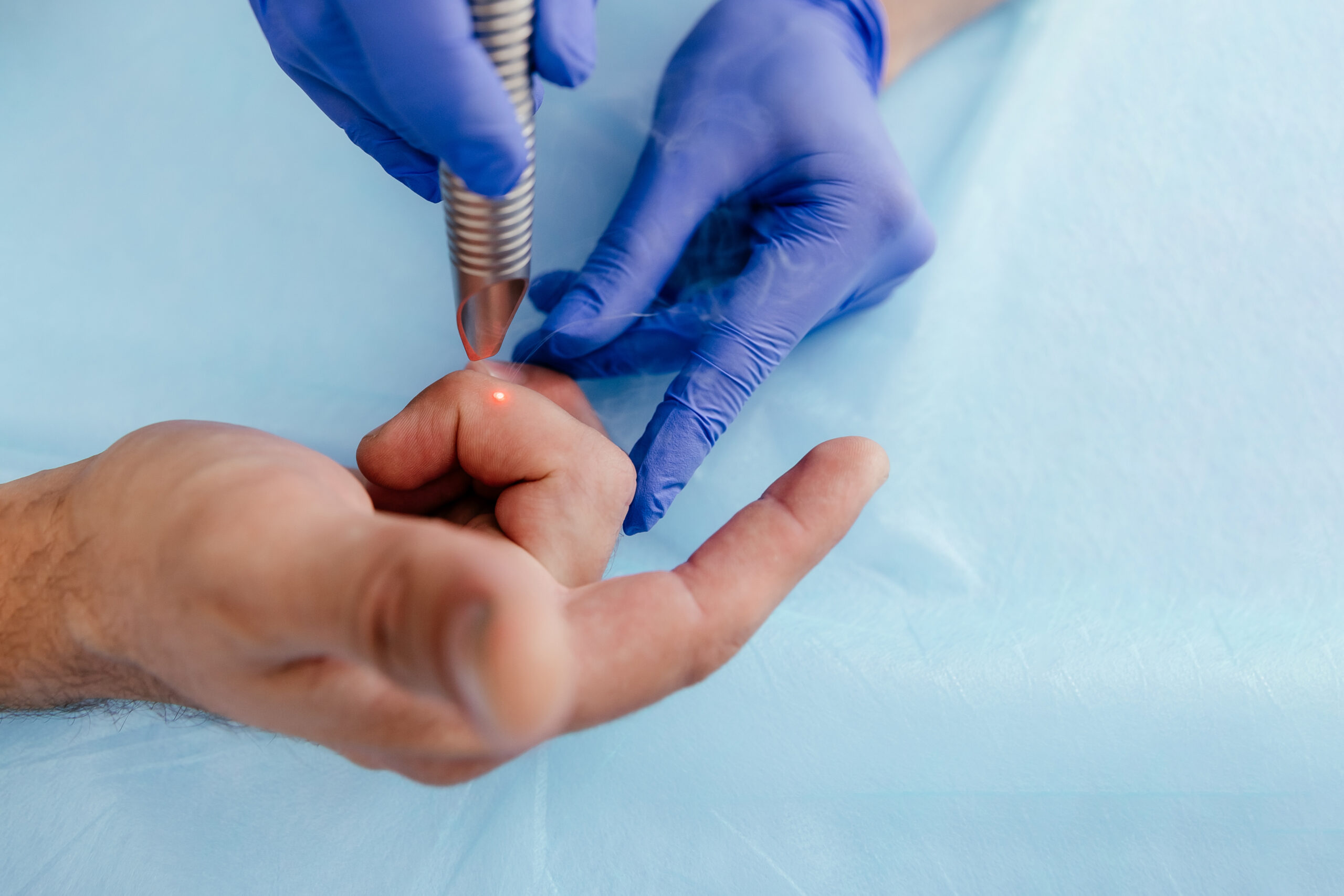
The most effective treatment option for viral warts is laser treatment. In the case of large warts, it may be necessary to first remove them superficially – e.g. with a sharp spoon – after a short pre-treatment with an anesthetic ointment.
The ablative function of the laser then gently removes the wart and the heat destroys the remaining virus particles under the skin.
Follow-up treatment with a prescription solution is often necessary to increase the success of treatment after laser treatment and to prevent recurrence of the warts.
Our private practice at Schweizer Platz in Frankfurt specializes in laser treatments and wart removal. Make an appointment now and have viral warts treated effectively.
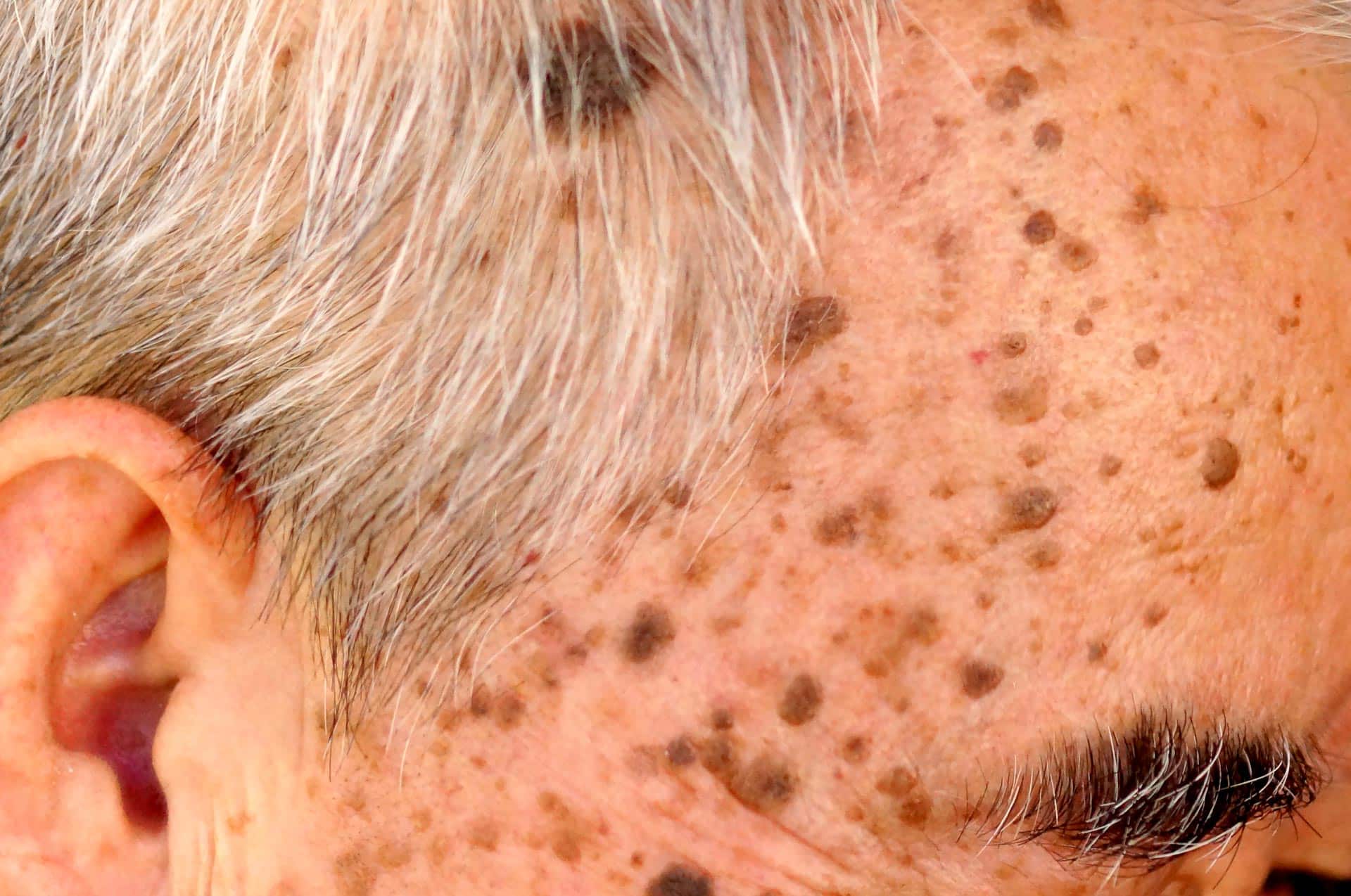
Age warts (Verruca seborrhoica)
Age warts are black or brown pigmented skin lesions with a fissured surface that usually occur in older patients.
These are microscopically so-called horn cysts and horn pearls, which store pigment but do not produce any pigment themselves. It is important to distinguish these age-related warts from melanoma (black skin cancer).
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture (below).
Wart laser treatment - remove old warts
The most effective treatment option for age-related warts is to remove the wart with a laser. In the case of large (age) warts, it may be necessary to first remove them superficially – e.g. with a sharp spoon – after a short pre-treatment with an anesthetic ointment.
The wart is then gently removed using the ablative function of the laser.
Treatment of benign skin changes with the Erbium:YAG laser
The Erbium: YAG laser is particularly suitable for the removal of benign skin lesions such as :
- Actinic keratoses (precursor of white skin cancer)
- Wrinkles and scars (incl. acne scars)
- Nail fungus
- Fat deposits on the eyelids (xanthelasma)
- Fibromas
- Benign birthmarks
- Wrinkle treatment and skin rejuvenation
- Upper and lower eyelid lift
The Erbium: YAG laser is the gold standard for highly precise, fully ablative or fractional ablation of the skin.
The laser is used for surgical treatment and is well suited to selectively removing unwanted tissue without damaging surrounding tissue. Erbium laser treatment does not leave any scars on superficial skin changes.
The treated skin areas are treated with a plaster or a small bandage after the procedure. Over the next few days, a crust forms, which falls off after about 10 days, so that the wound healing is completed with new skin tissue.
The use of the erbium laser in fractional mode for non-surgical upper and lower eyelid tightening, facial skin rejuvenation and the treatment of acne scars has a similar effect.